Introduction
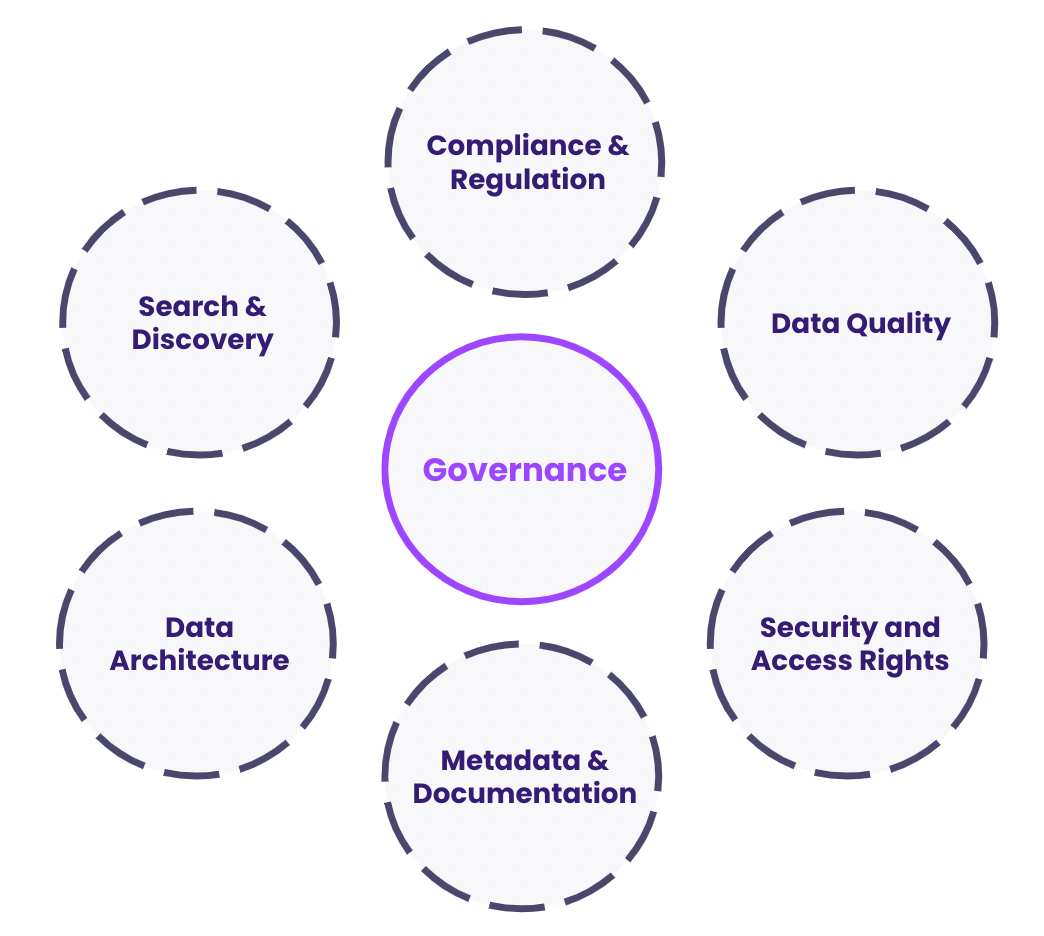
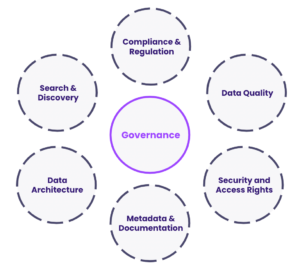
In any robust ERP data governance framework, defining roles and responsibilities is essential. Data ownership and stewardship ensure accountability, improve data quality, and promote efficient decision-making. This article delves into the concepts of data ownership and stewardship, outlines best practices for assigning these roles, and explores tools and techniques for effective implementation.
What are Data Ownership and Stewardship in ERP Systems?
Data Ownership:
The individual or team accountable for the quality, security, and compliance of a specific dataset. Owners define policies, resolve disputes, and oversee the data’s lifecycle.
Data ownership refers to the assignment of responsibility for specific data sets or entities within an ERP system. Owners are accountable for the accuracy, security, and lifecycle management of the data they oversee.
Key Responsibilities of Data Owners:
- Ensuring data integrity and compliance with organizational and regulatory standards.
- Approving changes to the data, including updates, deletions, and additions.
- Collaborating with other stakeholders to resolve data quality issues.
- Defining access rights and permissions for their data sets.
Benefits of Clear Data Ownership:
- Enhanced Accountability: Every data element has a responsible party, ensuring fewer errors and quicker resolutions.
- Improved Data Quality: Ownership ensures regular monitoring and updates, reducing inconsistencies.
- Stronger Security: Owners can define and enforce strict access controls to protect sensitive information.
Data Stewardship:
Stewards are responsible for implementing the data policies defined by the owners. They manage day-to-day operations like data entry, updates, and validation to ensure adherence to governance standards.
Data stewardship complements data ownership by focusing on the day-to-day management and maintenance of data within ERP systems. While data owners define the rules and standards, stewards ensure these are followed.
Key Responsibilities of Data Stewards:
- Monitoring data quality and implementing data cleansing activities.
- Enforcing data governance policies and best practices.
- Providing support during data integration, migration, and reporting activities.
- Training users on proper data handling and governance protocols.
Benefits of Effective Data Stewardship:
- Consistency Across Systems: Stewards ensure uniform data standards across integrated platforms.
- Operational Efficiency: Clean and well-maintained data reduces downtime and errors in processes.
- Proactive Governance: Stewards help enforce governance frameworks, ensuring compliance and best practices.
The Relationship Between Data Owners and Stewards
Data ownership and stewardship are complementary roles that work together to manage and govern data effectively. While owners set the strategic direction, stewards operationalize it by ensuring day-to-day adherence to policies and standards.
Example:
- Owner’s Role: Approves a data retention policy for customer records.
- Steward’s Role: Ensures customer records older than the retention period are archived or deleted in compliance with the policy.
Why Data Ownership and Stewardship Matter
- Accountability: Clear roles reduce ambiguity and ensure someone is always responsible for data quality.
- Efficiency: Streamlined roles help identify and resolve data issues quickly.
- Consistency: Owners and stewards ensure that data adheres to enterprise-wide standards.
- Compliance: Assigning accountability ensures that regulatory requirements are consistently met.
Best Practices for Assigning Data Ownership and Stewardship
1. Identify Key Data Domains
- Segment data into domains like customer data, financial data, and supplier data.
- Assign ownership to individuals with expertise in each domain.
2. Define Clear Roles and Responsibilities
- Owners: Focus on strategic oversight, policy definition, and decision-making.
- Stewards: Handle operational tasks like data cleansing, entry, and validation.
3. Provide Training and Support
- Offer training on governance tools and processes to ensure that roles are effectively executed.
4. Establish Collaboration Mechanisms
- Encourage collaboration between owners and stewards for alignment on governance goals.
5. Monitor and Measure Performance
- Use KPIs to evaluate the effectiveness of data governance roles, such as error rates and policy adherence.
Tools for Managing Data Ownership and Stewardship
- SAP Master Data Governance (MDG):
- Centralized platform for managing master data across domains.
- Enables role-based workflows and governance controls.
- Oracle Enterprise Data Management (EDM):
- Streamlines data ownership and change management processes.
- Facilitates collaboration between data owners and stewards.
- Collibra Data Governance Center:
- Provides a repository for documenting ownership and stewardship roles.
- Offers automated workflows to enforce governance policies.
- Informatica Data Governance:
- Focuses on data quality and lineage tracking to ensure accountability.
- Includes dashboards for monitoring governance activities.
Techniques for Effective Role Assignment
- RACI Matrix:
- Define who is Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed for each data activity.
- Ensures clarity in ownership and operational responsibilities.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC):
- Use access control mechanisms to ensure owners and stewards can only manage relevant data.
- Regular Reviews:
- Periodically review roles and responsibilities to accommodate organizational changes.
Challenges in Defining Roles and How to Overcome Them
| Challenge | Solution |
|---|---|
| Overlapping Responsibilities | Clearly define scope and responsibilities using RACI matrices. |
| Lack of Accountability | Assign performance KPIs and use dashboards to track role effectiveness. |
| Resistance to Change | Provide training and communicate the benefits of role-based governance. |
Conclusion
Defining data ownership and stewardship is essential for a successful ERP data governance framework. By assigning clear roles, leveraging the right tools, and fostering collaboration, organizations can ensure data quality, compliance, and efficiency.
Know more about Mastering Data Governance In our Previous Article and Stay Tuned for the Next Article on Establishing Data Standards and Policies in ERP Data Governance