Introduction
Data governance is the cornerstone of effective ERP data management, ensuring data accuracy, consistency, and security across an enterprise. Without a solid governance framework, businesses risk data silos, compliance violations, and operational inefficiencies. This article explores the fundamentals of data governance in ERP systems, its importance, and actionable steps to establish a robust foundation.
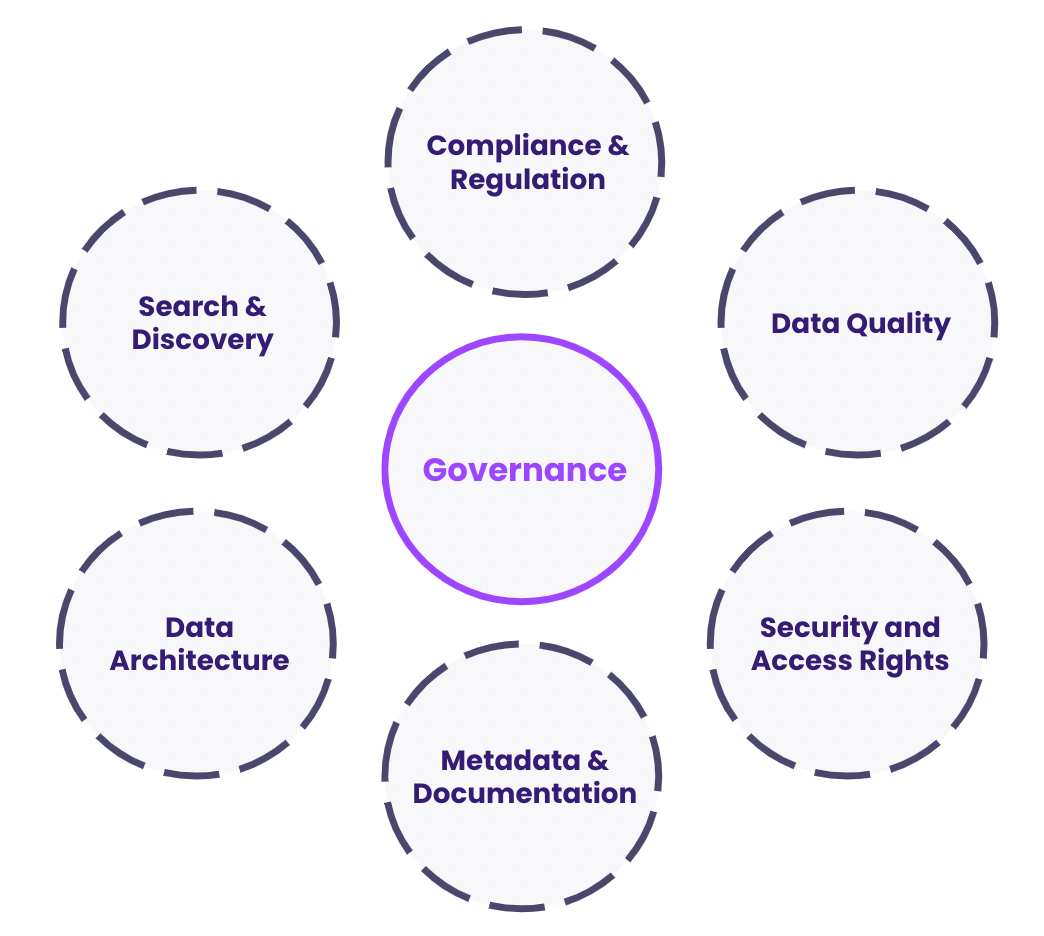
What is Data Governance in ERP?
Data governance involves setting policies, procedures, and standards for managing enterprise data effectively. In ERP systems, it ensures that data is:
Accurate: Free from errors and inconsistencies.
Accessible: Available to authorized users when needed.
Secure: Protected against unauthorized access and breaches.
Compliant: Aligned with industry and government regulations, such as GDPR or CCPA.
Why Data Governance is Critical for ERP Success
- Supports Decision-Making: Accurate, well-managed data leads to better strategic decisions.
- Enhances Efficiency: Reduces data redundancies and inconsistencies, streamlining processes.
- Ensures Compliance: Aligns data handling with regulatory requirements, avoiding penalties.
- Promotes Data Ownership: Establishes accountability, ensuring data integrity.
Steps to Build a Data Governance Foundation in ERP
1. Define Objectives and Scope
- Objective: Identify what the governance framework aims to achieve, e.g., improved data quality or compliance.
- Scope: Decide which data domains (e.g., master data, transactional data) are included.
2. Assign Roles and Responsibilities
- Data Owners: Accountable for the quality and security of their data domain.
- Data Stewards: Manage day-to-day data operations, ensuring policies are followed.
- Data Governance Committee: Oversees the framework and resolves conflicts.
3. Develop Governance Policies and Standards
- Create guidelines for data entry, updates, and deletions.
- Define validation rules to ensure accuracy.
- Establish retention policies to manage lifecycle and archival.
4. Select Supporting Tools
Tools can automate and simplify data governance processes. Examples include:
- SAP Information Steward: Ensures data quality and compliance.
- Oracle Enterprise Data Management (EDM): Manages master and reference data.
- Collibra Data Governance Center: Offers workflows for policy enforcement and compliance tracking.
5. Conduct Training and Change Management
- Train employees on governance policies and tools.
- Communicate the benefits of governance to drive adoption.
Techniques for Effective Data Governance in ERP
- Data Audits: Regularly audit data for quality and compliance gaps.
- Data Mapping: Understand how data flows across systems to identify inconsistencies.
- Data Lineage Tracking: Monitor data from creation to consumption, ensuring accountability.
| Challenge | Solution |
| Resistance to Change | Involve key stakeholders early and demonstrate value through pilot programs. |
| Lack of Resources | Start small with critical data domains before scaling the governance framework. |
| Complex Regulatory Requirements | Use automated compliance tools to track and enforce standards. |
Conclusion
Establishing a solid foundation for data governance in ERP systems is essential for maintaining data integrity, enabling informed decision-making, and ensuring compliance. By following the steps and leveraging the tools discussed, businesses can create a governance framework that supports sustainable growth.
4 thoughts on “Mastering Data Governance in ERP: Building a Strong Foundation”